EFFICACY
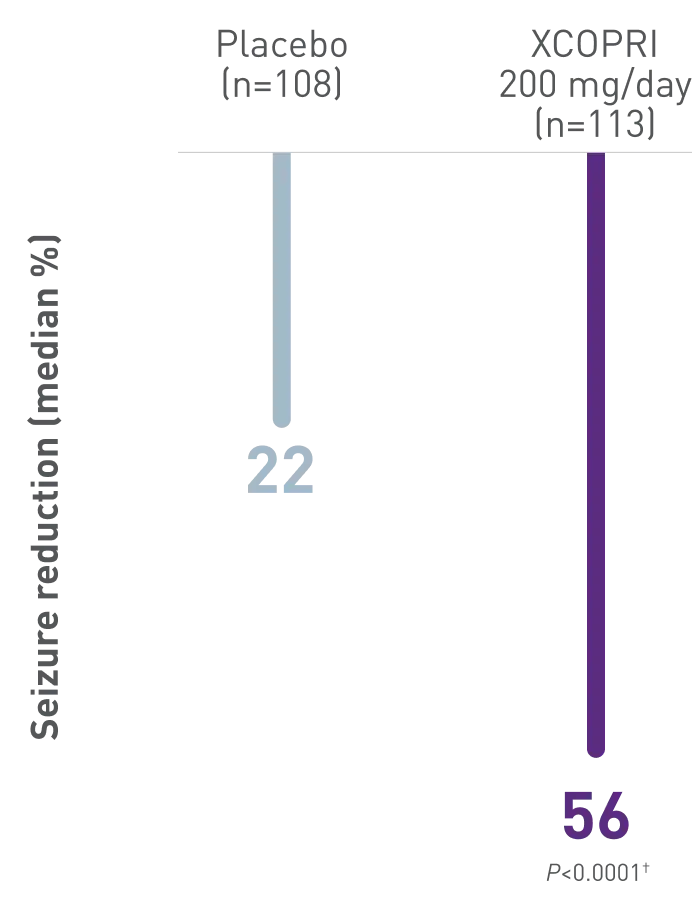
XCOPRI efficacy data for partial-onset seizure reduction
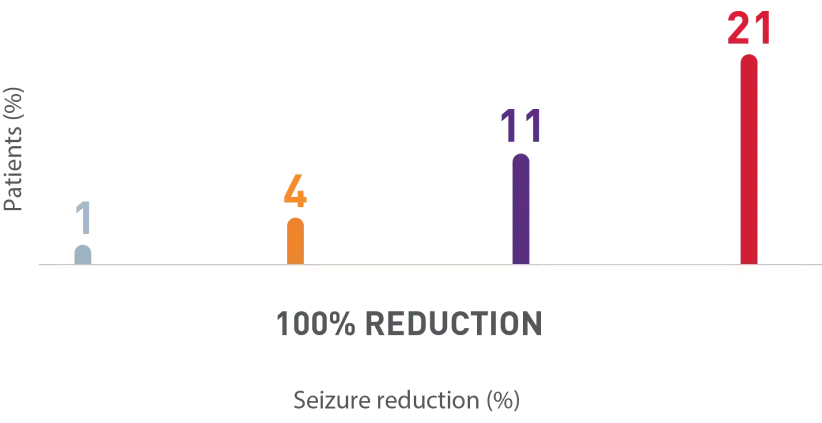
ZERO seizures with XCOPRI is possible1
In a study of adult patients with a median of 9 seizures/28 days at baseline
Primary
Outcome
Patients experienced up to 2x greater seizure reduction with XCOPRI compared with placebo (55% XCOPRI 400 mg, 55% XCOPRI 200 mg, 36% XCOPRI 100 mg vs 24% placebo)1
AS MANY AS 1 IN 5 PATIENTS EXPERIENCED ZERO SEIZURES1
Secondary
Outcome
Percentage of patients who achieved seizure reductions of 100% (12-week, maintenance phase)1,2
Zero seizure rates achieved within the first 4 weeks and increased over time
Post-hoc analysis of an open-label study: Percentage of patients with 1-2 seizures/28 days at baseline who achieved zero seizures during first 4 weeks1
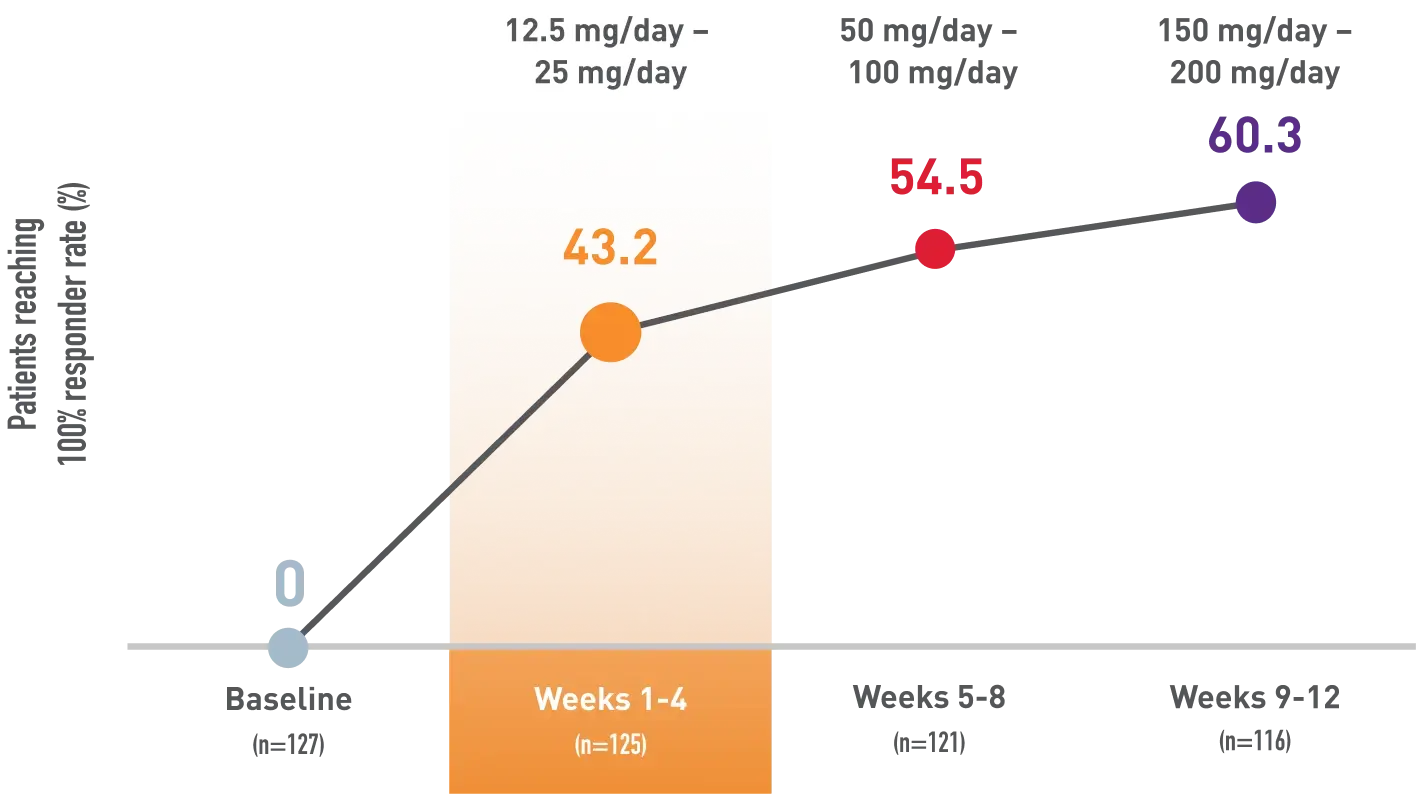
Weeks of titration
Limitations
This post-hoc analysis of an open-label study of XCOPRI did not include a control arm. These data are descriptive and representative of an enriched population with a relatively small number of patients. Appropriate multiplicity adjustments were not applied.
Long-term zero seizure rates for 12 months or longer
Post-hoc analysis of an open-label study: Patients with 1-2 seizures/28 days at baseline who achieved zero seizures for ≥12 months1


Limitations
This post-hoc analysis of an open-label study of XCOPRI did not include a control arm. These data are descriptive and representative of an enriched population with a relatively small number of patients. Appropriate multiplicity adjustments were not applied.
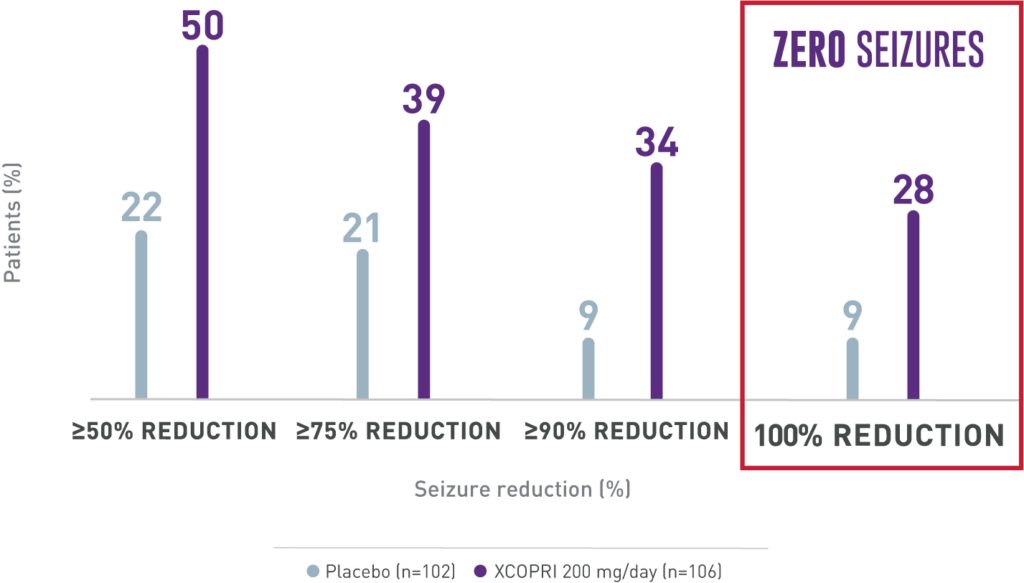
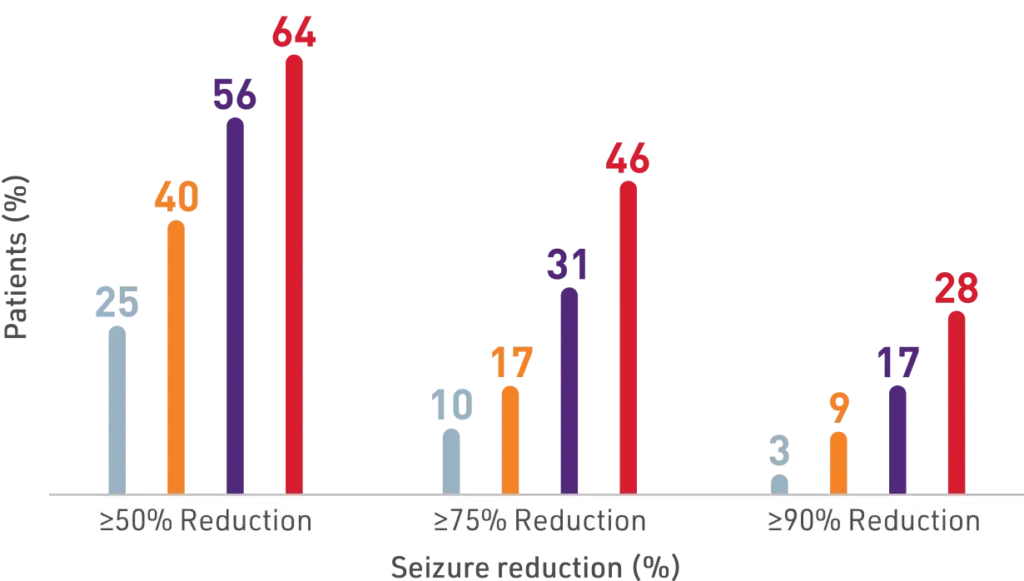
Significant seizure reduction with XCOPRI
Secondary Outcome
Percentage of patients who achieved seizure reductions of ≥50%, ≥75%, and ≥90% (12-week, maintenance phase)1,2
Demonstrated to be effective in multiple types of partial-onset seizures2-4
XCOPRI demonstrated reductions in seizure frequency across multiple types of partial-onset seizures compared with placebo2-4
Secondary Outcome
Median percentage reduction in 28-day seizure frequency in partial-onset seizure subtypes (12-week, maintenance phase)2,3
PARTIAL-ONSET
SEIZURE SUBTYPE
Placebo
XCOPRI
100 mg/day
XCOPRI
200 mg/day
XCOPRI
400 mg/day
Simple partial
seizures*†
11%
(n=17)
49%
(n=21)
62%
(n=24)
69%
(n=20)
Complex partial
seizures*
29%
(n=87)
32%
(n=95)
55%
(n=87)
62%
(n=86)
Secondary generalized
tonic-clonic seizures*
33%
(n=43)
51%
(n=34)
92%
(n=32)
83%
(n=36)
Contact a rep
Request SamplesRead more about XCOPRI’s safety.